Scientific Name of Apes
Apes are the most man-like of all animals. In fact, man is classed biologically with the apes in the anthropoid group. The scientific name of ape is Hominoidea. Unlike monkeys, apes have no tails. They are generally larger than monkeys. In general form, apes’ bodies are much like man’s, but their arms are longer and the legs shorter in proportion than a man’s. Except for their faces, hands, and feet, apes are covered with hair.

What most distinguishes the apes from other animals is their brain. They are the most intelligent creatures in the world apart from man. In captivity, they may acquire many almost-human habits. They can solve quite difficult ‘problems’ and can use sticks as primitive tools – to pull something within reach, for instance. In all apes, the coordination of hand and eye is well developed. They can use both hands and feet as we use our hands, to hold objects and do things. There are four main types of apes, divided into two groups. The lesser apes comprise several species of gibbons. The more advanced great apes include the orangutan, chimpanzee, and gorilla. Chimpanzees and gorillas live only in Africa; the other species live in Asia. They all live in groups in forests and eat fruit and other plant food.
- Gibbon scientific name is Hylobatidae
- Orangutan scientific name is Pongo
- Chimpanzee scientific name is Pan troglodytes
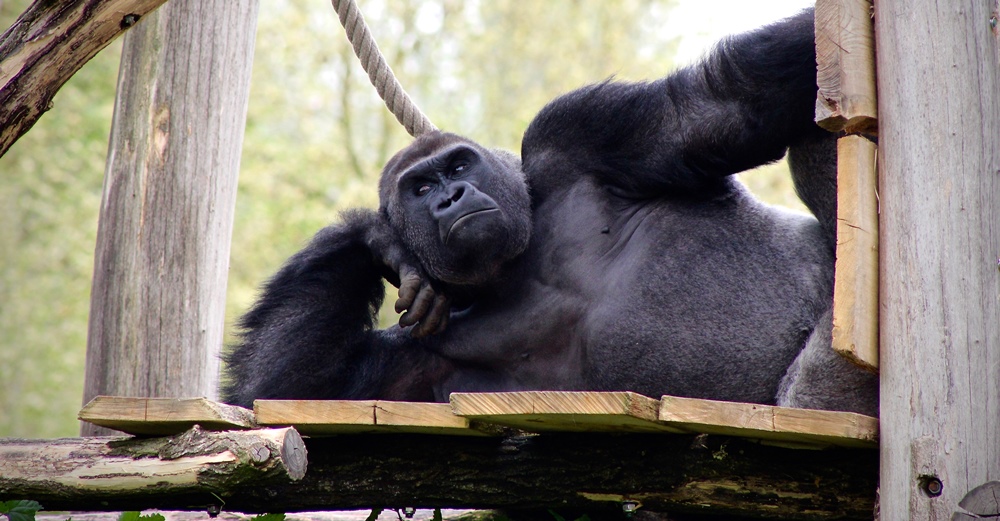
- Gorilla scientific name is Gorilla
Gorillas are by far the largest of the apes. They stand as high as a man and may weigh up to 600 lbs. Gorillas are also immensely strong. Both gorillas and chimpanzees live and move about on the ground, climbing to platforms built in trees to sleep. Chimpanzees can also swing from tree to tree, however. They are extremely intelligent animals and have great curiosity. They love exploring.
Orangutans are the only apes to live entirely in trees; they swing from branch to branch in the forests of Sumatra and Borneo, in Indonesia. Their name means ‘man of the woods’ and they may look remarkably human. Gibbons can also travel at great speed through the forests. They have extremely long arms and are smaller and lighter than the other apes.