Where do elephants live ?
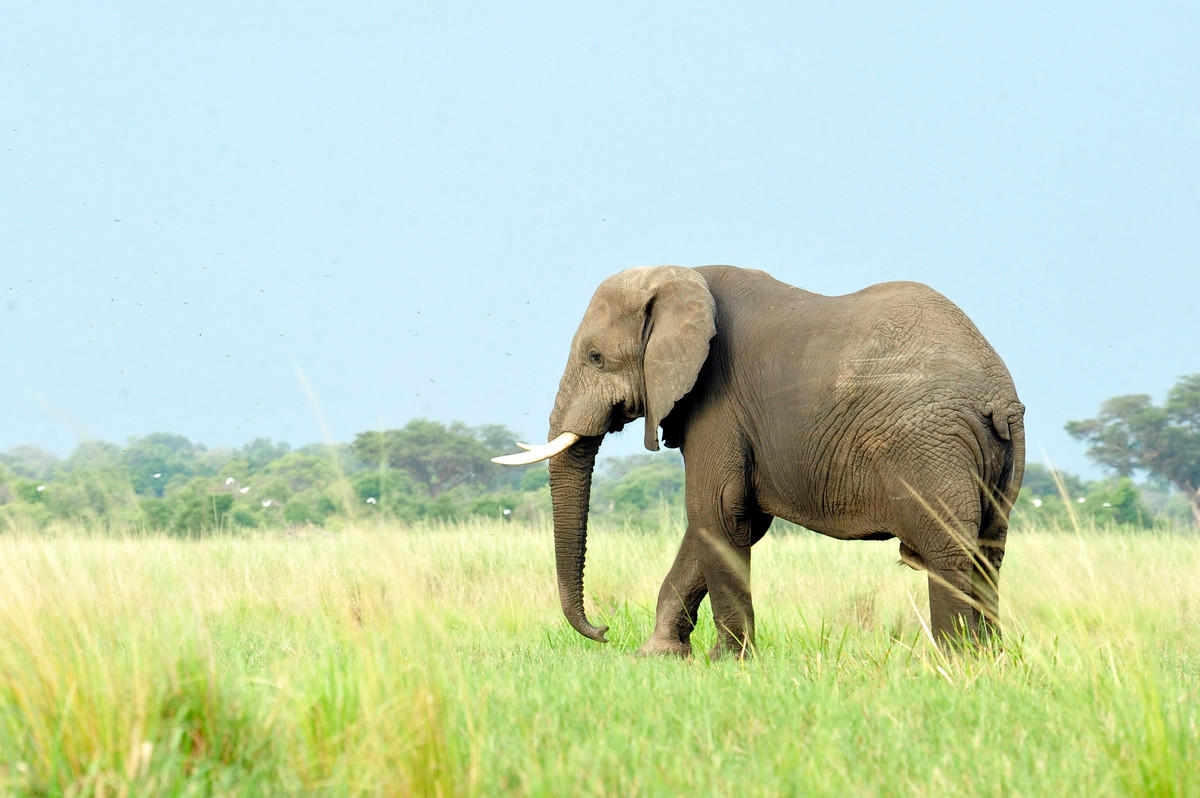
 Once African elephants inhabited almost the entire African continent. The habitat of elephants was stretched from the north to the south of the whole continent. As early as the 6th century of our era, the northern population of elephants was completely exterminated.
Once African elephants inhabited almost the entire African continent. The habitat of elephants was stretched from the north to the south of the whole continent. As early as the 6th century of our era, the northern population of elephants was completely exterminated.
In the 21st century, the African elephant population has been preserved in the southern, western, eastern and central African countries, namely: Namibia, Tanzania, Senegal, Burkina Faso, Kenya, South Africa, Mali, Botswana, Ethiopia, Chad, Zimbabwe, Somalia, Angola, Guinea Bissau, Zambia, Uganda, Botswana, Niger, Guinea, Ghana, Rwanda, Liberia, Cameroon, Benin, Sierra Leone, Togo, Congo, Malawi, Mozambique, Côte d’Ivoire, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Sudan, Eritrea, Gabon, Swaziland, CAR, Equatorial Guinea. Most of the livestock, in these countries, live in the territories of reserves and national parks. Going beyond the reserves, elephants often become the prey of poachers.
African elephants inhabit different landscapes, avoiding only deserts and tropical forests. The main priorities for choosing places of residence for elephants are such criteria: the availability of food resources, water and shade.
Where does the Indian elephant live?
The Indian elephant was spread throughout South Asia. In the wild, he lived along the rivers Tigris and Euphrates until the Malay Peninsula. Some herds were distributed even near the Himalayas and along the Yangtze River, which is in China. In addition to the continental part of Asia, elephants inhabited the islands of Sumatra, Sri Lanka and Java.
Now the Asian elephant is found in the wild only partially in the Northeast and South India, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Malaysia (Borneo), Nepal, Cambodia, Laos, Indonesia (o.Sumatra), China, Bangladesh, Vietnam, Myanmar, Brunei and Laos.