What is Mesothelioma?
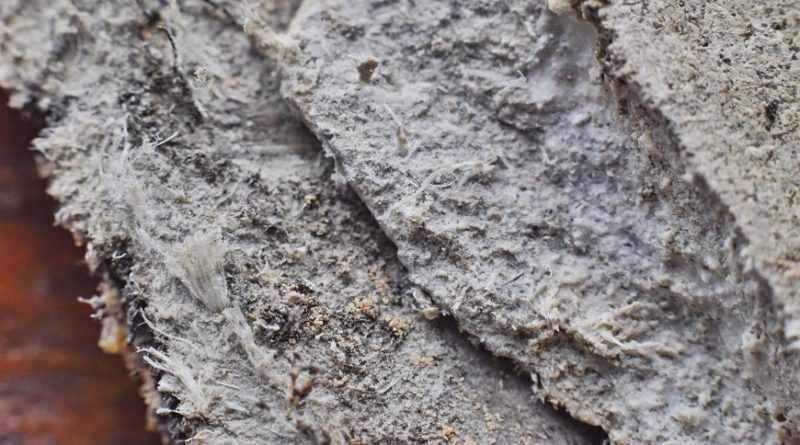
The tumour of the pleura or the lining of the lungs is called mesothelioma. This tumour may be cancerous or non-cancerous. Exposure to asbestos is the commonest cause of this condition. Among patients with malignant or cancerous pleural mesothelioma, 77% have previously been exposed to asbestos. This is a chronic condition that occurs due to years of exposure to asbestos. Very fine fibres of asbestos that are suspended in the air are inhaled accidentally, usually due to occupational exposure. These fibres settle in the lungs and cause low grade or chronic inflammation. This may result in genetic mutations in the cells of the lungs or pleura and the development of cancer.
Asbestos and mesothelioma
The crocidolite and amosite asbestos is the carcinogen primarily implicated in the genesis of malignant pleural mesothelioma. This occupational disease is seen in people working in asbestos mills, shipping yards and mines. The industries like shipbuilding, ceramics, asbestos cement manufacture, asbestos brake lining manufacture, railroad repair and insulation have a high incidence of asbestos-related diseases including mesothelioma.
Clinical features
This cancer is more commonly seen in men than women with a ratio of 3:1. The peak incidence occurs during the 5th to 7th decade of life. Difficulty in breathing and chest pain are the common symptoms seen in the majority of people suffering from pleural mesothelioma. The other features include chest discomfort, fever with sweating, easy fatigability and loss of weight. Many of these patients develop a collection of fluid in the chest called pleural effusion. This fluid compresses the lungs and adds to the discomfort and breathing difficulty though a few may remain asymptomatic.
Mesothelioma diagnosis
Pleural effusion is detected on taking chest radiographs. This may also demonstrate nodular thickening of the pleura, involvement of the diaphragm, and a reduction in the size of the affected part of the chest.
The diagnosis is confirmed by thoracoscopic biopsy. In this procedure, a telescope is passed into the chest and a small tissue from the pleura is removed. This shows evidence of mesothelioma on microscopic examination. The cancer cells of mesothelioma are also seen in the pleural effusion fluid that is aspirated with a syringe, called thoracentesis, and is examined microscopically. Diagnosis is difficult because results from fluid analysis of the tumor’s effusion are not usually diagnostic whereas thoracoscopic biopsy is positive in 98% of cases.
Management of mesothelioma
A multimodality method is used for the management of these patients as there is a better response with such a multipronged approach. The options include surgical resection, radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Some of the drugs used in chemotherapy include Cisplatin, gemcitabine, and pemetrexed. Death in these cases is usually due to chest infection or respiratory failure.
Prognosis
Once this cancer develops, the chances of survival are very bleak. A person may live for another 6 to 8 months without treatment. With the treatment, life may extend by one to one and a half years. Even after surgery, the tumor may recur in more than 50% of people.
This cancer is difficult to diagnose, therefore a high index of suspicion is essential especially in people working in high-risk industries. A regular health check-up is essential to help in the early diagnosis and treatment. Prevention is always better and care should be taken as per the industry guidelines against inhalation of asbestos in the prone environment.