Are pregnancy tests reliable?
Pregnancy tests are commonly used to detect pregnancy soon after a woman discovers that her period is missing. The concern about getting pregnant or not getting pregnant has resulted in an enormous use of pregnancy tests. Although many brands sell their kits, their accuracy may be different and they might not always be reliable. The interpretation of these tests is simple, however, it may at times require an expert opinion or other modalities of investigation.
Pregnancy hormone
All pregnancy tests are based on the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), commonly known as a pregnancy hormone, in the urine or in blood. This hormone is produced in excessive amounts by the developing placenta in the uterus and released in the blood circulation of a pregnant woman. HCG is produced almost exclusively in the placenta but it is also synthesized in fetal kidneys and a number of fetal tissues. Apart from that, hCG is produced in very small amounts in tissues of men and non-pregnant women in the anterior pituitary gland and in large quantities by tumors of the placenta but the detection of hCG in blood or urine is almost always indicative of a pregnancy.
Basis of pregnancy test
Pregnancy hormone is a glycoprotein with a high carbohydrate content. It is composed of two subunits called α and β. The α-subunit is similar to many other hormones present in human blood, like luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), or thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). Since the β-subunit is unique, antibodies were developed with high specificity for this subunit of hCG. This specificity is the basis for the detection of hCG in urine or blood. Numerous commercial test kits are available for measuring serum and urine levels of hCG. Each test uses a slightly different combination of antibodies and hence its sensitivity and reliability for detecting pregnancy are different. Although each detects a slightly different mixture of a hormone, its free subunits, or its metabolites, all of these immunoassays are appropriate for normal pregnancy testing. With these sensitive tests, the hormone can be detected in maternal plasma or urine by 8 to 9 days after insemination.
Urine and blood tests
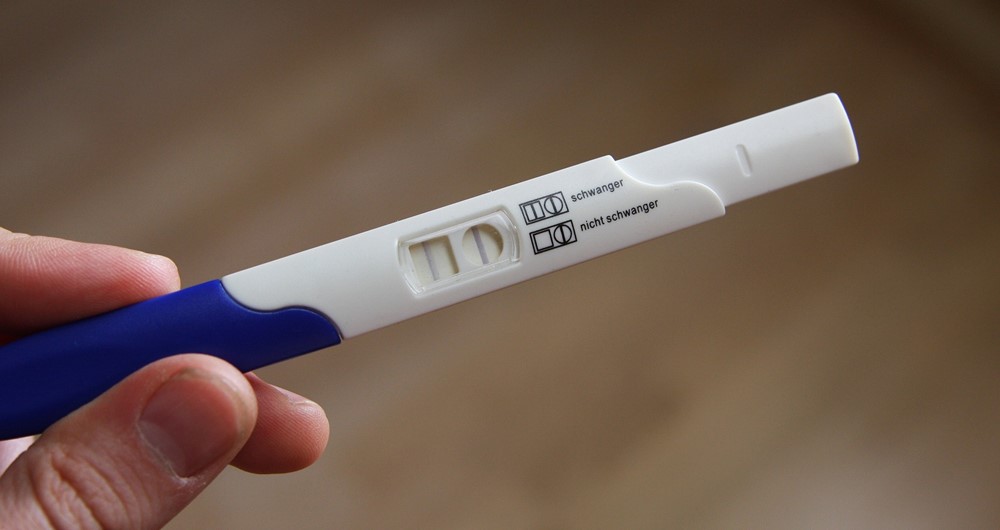
Tests done on urine are called ‘Home pregnancy tests’ and they can confirm a pregnancy prior to the missed period. They are inexpensive, easy to do, and can be done at home. Home pregnancy test kits are easily available and sold over the counter. They are performed with a simple in-use indicator slide on which urine is dropped. A positive test is indicated by the appearance of a colored line on the indicator. Their results are said to be reliable when done 8-9 days after insemination.
Pregnancy tests using blood are done in a lab or by the physician. They are more accurate than the home tests, as their sensitivity is much higher. Results of these tests are reliable when performed 5-7 days after insemination.
Reliability of pregnancy tests
Though most of the tests claim 99% accuracy of pregnancy detection, it may not be the case. Research in clinical trials revealed that a detection limit of 12.5 mIU/mL hCG is required to diagnose 95 percent of pregnancies at the time of missed period. The accuracy and reliability of 18 different home pregnancy tests were assessed and it was found that only one brand had this degree of sensitivity. Two other brands gave false-positive or invalid results. A clearly positive result was given by only 44 percent of the brands at an hCG concentration of 100 mIU/mL. With this level of sensitivity, only about 15 percent of pregnancies would be identified at the time of missed periods. Commonly available pregnancy tests sensitivity vary from 20mIU/mL to 100mIU/mL hCG. By using tests with higher sensitivity (eg. 20mIU/mL) you should be able to detect pregnancy sooner than using those less sensitive.
False-positive result
False-positive hCG test results are rare. Sometimes women may have factors in their blood that may interact with the hCG antibody. These factors may develop in women who have worked closely with animals and were found to develop antibodies to animal antigens in their blood. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists has suggested alternative laboratory techniques if such antibodies are suspected.
A missed period is of great concern to any female. It may be a cause for celebration or a cause for concern and worry. At a young age, with active sexual life, the positive result of a pregnancy test is almost always related to the occurrence of pregnancy and the results should be treated as very reliable. Though there are a lot of pregnancy tests available on the market, a positive or negative result after a missed period should be interpreted carefully. A gynecologist should be consulted whenever periods are missed, positive pregnancy test result occurs or morning sickness develops.