How often should you do a blood test?
A blood test is a laboratory test performed on a sample of blood. This is done for diagnosis of a disorder or alterations produced in the blood composition in certain diseases and acute conditions. Blood is a vital fluid that carries oxygen and nutrients to all organs and also carries metabolic products for excretion by the kidneys and other organs. A suitable range of these components is maintained normally.
How much blood is lost for a test?
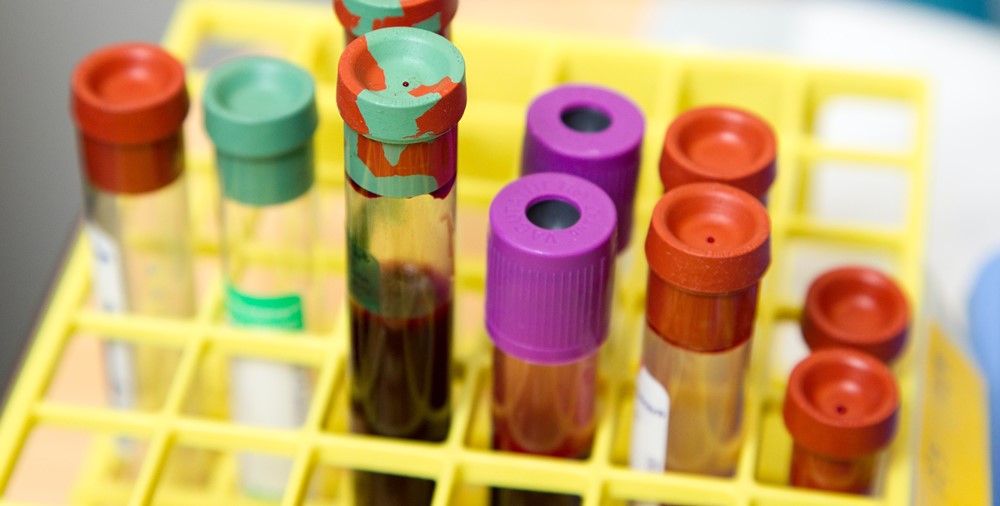
Whenever a blood test is required, a sample of blood is collected from a vein in the forearm or back of the hand. Depending on the number of tests to be performed, usually, 10 to 50 ml of blood sample is collected in multiple bottles. This amount of blood is very small in relation to the total amount of blood in the human body. It does not result in any deficiency or weakness.
Blood components
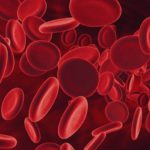
Blood is composed of solid and liquid components. The solid component includes cells and the liquid part is plasma. Plasma contains enzymes, minerals, lipids, hormones, sugars, vitamins and proteins. The blood cells include red blood cells which transport oxygen from the lungs to the tissues and carbon dioxide from tissues to the lungs; white blood cells defend the body against infections and platelets help in clot formation in case of bleeding from injury.
Method of testing blood
The patient should be on an empty stomach because the food consumed before a test may affect the results. The test is performed in a laboratory in the morning. The results of a blood test help in finding any abnormal substances present in the body. It is also important to understand if a person has normal reports as it reassures a person in case of any doubt. Most of the reports are done in highly sophisticated machines and the procedure is automated. This reduces the chances of false reporting. Also, a test should not be done after severe physical exertion because many values could be deranged due to hemodynamic changes and changes in blood composition.
How often should a blood test be performed?
Depending on the age of a person and their health status, a blood test should be performed monthly to quarterly. Some of the tests are done half-yearly or annually. After the age of forty years, annual blood and urine profile is done as a screening test in a healthy population. In case of any suspicion, further investigations are done to rule out any serious illness.
Diabetes mellitus: Blood sugar monitoring is required many times a day in case of an acute complication like an infection. Once the condition is stabilized, monthly blood sugar estimation may be adequate.
Thyroid disorders: A blood test is done if hypo or hyperfunction of the thyroid gland is suspected. Initially, a fortnightly assessment may be required to bring thyroid status to normal. Once achieved, a six-monthly and later annual check on patients with maintenance therapy is adequate.
Liver and kidney disorders: They also require frequent monitoring in an acute setting like liver or kidney failure. Later on, when the condition improves, a monthly test usually suffices.
Obesity: These people require testing of their lipid profile as a baseline investigation. During weight reduction with dieting, exercise or drugs, a monthly test is done.
HIV testing: During childbearing age, a test for HIV is done. Before any blood donation also, this test is mandatory.
The other time when a complete profile of blood tests is done is before any major surgery. As surgery itself adds to the stress, all tests are done with the aim of achieving an optimal state in order to achieve the best outcome of surgery.
Blood tests are important and should be done when indicated. The screening tests are done with a particular frequency whereas diagnostic tests are done when a person develops symptoms of a disease. While giving samples of blood, one should ensure that adequate precautions are taken for the prevention of transmission of diseases like AIDS and hepatitis.