Backache during pregnancy – how to prevent?
Back pain is one of the most common complaints during pregnancy with a prevalence varying from 48% to 76%. It is often treated as a minor and inevitable problem. The pain can be severe and that requires management under medical supervision.
Causes of backache
Back pain during pregnancy has multiple causes. Usually, it is due to excessive strain over paraspinal or back muscles. During mid-pregnancy and afterward, the uterus becomes heavier. This shifts the center of gravity upwards and forwards resulting in a change of posture. Most women lean backward assuming a posture of lordosis or increased backward curvature of the spine. This posture is maintained by increased activity of back muscles which develop spasms.
There is also some degree of weakness of abdominal muscles as they get overstretched. The hormones of pregnancy also cause the muscles to relax and become loose. This further aggravates the above posture as the balancing effect of abdominal muscles is not there.
Later in pregnancy, the joints of the spine and pelvis become lax due to the effect of pregnancy hormones estrogen and relaxin. This results in increased mobility of joints which is further aggravated by the weight of the growing fetus as well as maternal weight gain due to an increase in fat deposition. This causes generalized pain in the lower back, buttocks, and thighs. There is an increased risk of injury during exercise due to the above changes.
Treatment
The performance of regular mild exercises including back muscle exercise helps to strengthen these muscles, improves posture, and relieves spasms. These exercises also prepare the patient for labor and childbirth. In patients with persistent backache, a back brace or maternity sling may be used on the doctor’s advice. These appliances support the weight of the abdomen and relieve excessive loading of the spine. Bed rest, sitting in a warm bath, and physical therapy also provide relief.
Recommended exercises for back pain during pregnancy
- Pelvic tilt exercise: Place a floor mat. Then kneel down on hands and knees. In this position, the pelvis is tilted forwards and backward while keeping the buttocks relaxed.
- Backstretch: Come to the above-described position on a floor mat in an airy room. The legs should be kept apart and a small pillow should be placed under the abdomen. Then stretch arms forward on the floor to feel the stretch of the back.
- Hamstring Stretch: Place a foot on the chair seat while standing in front of it. Keeping the back straight, gently lean forward to stretch the back of the thigh.
Prevention
Preventive steps should be taken to avoid any aggravation of symptoms. One should make an attempt to maintain a normal posture while standing, sitting or walking. Some of the helpful tips are discussed here.
- Wear loose-fitting, low-heeled shoes with insole support for the arch.
- While standing, use a comfortably wide stance for better support and balance.
- Do not lift heavy objects.
- Do not stand for a longer period of time.
- Always sleep on a firm bed. Sleeping on a very soft bed may aggravate backache as it fails to provide support while sleeping.
- Do not bend over to pick up things from the floor. It is advisable to squat down by bending the knees while keeping the upper body straight.
- Sit with back support using a cushion or pillow.
- Sleep on the right or left side with a pillow between legs for support.
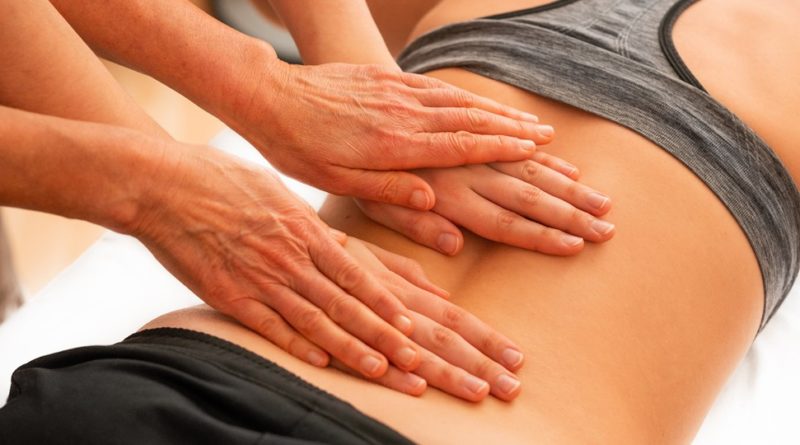
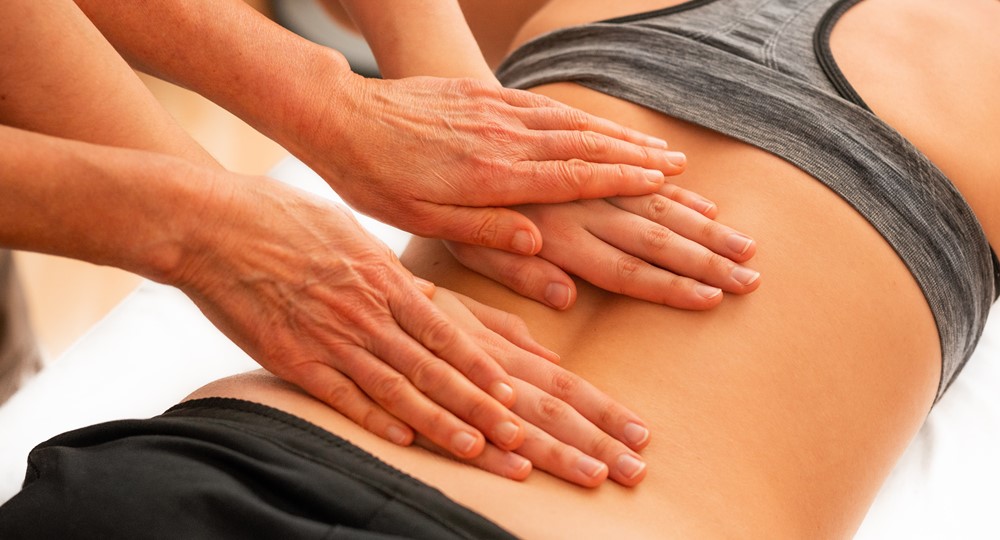
- Regular gentle massage of back muscles is recommended.
Low backache is a common problem during pregnancy. The symptoms are more severe in poorly nourished patients with weak musculature. One should plan for pregnancy with good nutrition and strengthening exercises before getting pregnant. A regular antenatal check-up with advice on nutrition and regular exercise helps in better pregnancy management.