10 Facts about Low Blood Pressure – Interesting and Useful Facts
Today we will check 10 interesting and useful facts about low blood pressure.
10 Facts about Low Blood Pressure
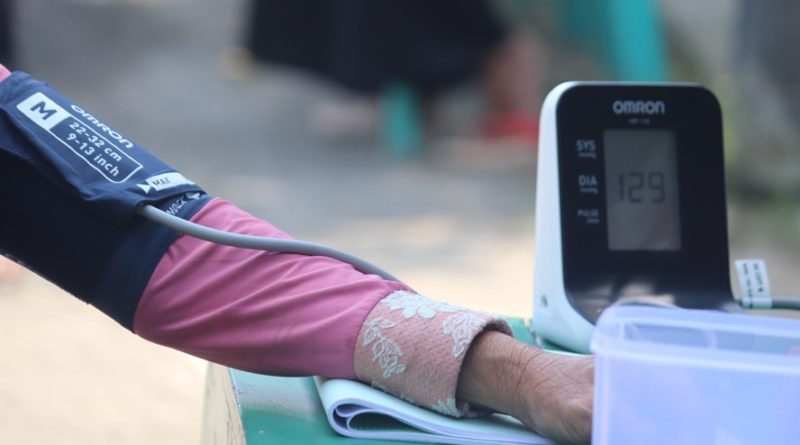
- The cause of low blood pressure can be assessed with blood tests, cardiac testing to look for arrhythmias, and radiologic studies.
- The many types of low blood pressure or hypotension are Postural (orthostatic) hypotension, multiple system atrophy with orthostatic hypotension, postprandial hypotension, neurally mediated hypotension, and nutritional deficiencies.
- Symptoms of reduced blood volume or low blood pressure also known as hypovolemia, are lightheadedness, chest pain, shortness of breath, headache, dysphagia, prolonged fatigue, and sometimes fainting and seizures.
- Another fact – if low blood pressure is diagnosed as postural hypotension, then treatment could include rehydration, changing time of meals, elevated bed, and pressure graded stockings and if low blood pressure does not show any signs or symptoms then it need not be treated.
- If diagnosed as neurally mediated low blood pressure, then the treatment includes not standing for long periods of time, avoiding emotional setbacks, plenty of fluids, increasing salt intake.
- Orthostatic low blood pressure is relatively common and has no impact on vascular or nonvascular mortality and hypotension does not have any criteria such as sex.
- Low Blood Pressure is considered more as a physiologic state than a disease and is usually associated with shock.
- Athletes, people who regularly exercise, people who maintain ideal body weight, and nonsmokers are likely to have low blood pressure and as long as there is no symptom, there is no concern.
- Orthostatic hypertension or low blood pressure caused by postural disturbances means the blood vessels do not adjust to a standing position and allow the blood pressure to drop which results in light-headedness.
- Another fact – multiple system atrophy with orthostatic hypertension is called Shy-Drager syndrome, and it is a rare disorder that causes progressive damage to the autonomic nervous system which controls involuntary functions such as blood pressure, heart rate, breathing, and digestion.