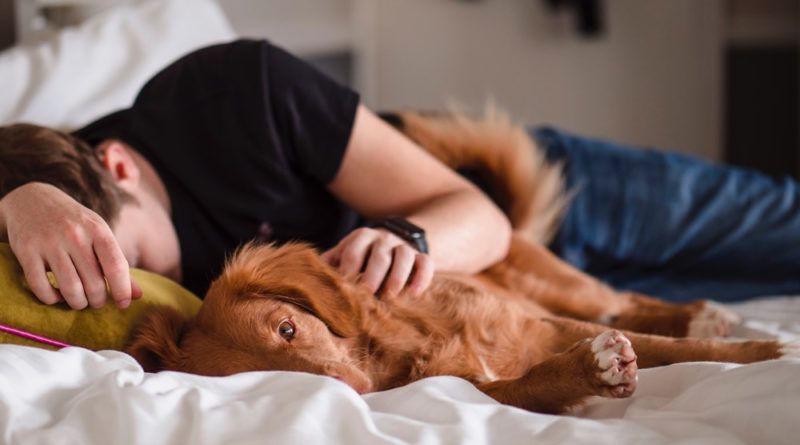
Why do people snore?
Snoring is a sound generated during sleep due to vibration of the upper airway. It occurs both during inspiration and expiration, though it is louder during inspiration. It is seen more commonly in men and is associated with sleep disorders in a majority of these people. In others, this occurs in isolation and is not related to any disorder.
Why does snoring occur?
When the flow of air through the upper airway gets obstructed, it results in increased resistance to flow. This causes vibration along the passage which causes the production of sound. The obstruction can exist due to various reasons described below.
Some people snore whenever they develop an allergy to pollens or a sinus infection. In these patients, the problem of snoring may be seasonal. Any deformity of the nose like deviated nasal septum or presence of nasal polyp can alter the airflow pattern by causing a partial obstruction. When the nasal septum, which separates the right from the left nostril, is deviated to one side, it results in distortion of the nasal passage. In the same way, the grape-like swellings of nasal mucosa or the polyps can cause obstruction especially in people with allergic disorders, and result in snoring.
The muscle tone of the airway may be poor in some patients. During sleep, the tongue tends to fall back causing airway obstruction. This may occur during deep sleep, after consumption of alcohol, or under deep sedation due to consumption of sleeping pills. Aging can add to these effects due to the increased laxity of tissues.
Children have enlarged tonsils in the throat or adenoids in the nasopharynx. Their enlargement is related to allergy or infection. This can result in snoring and is an important cause in children.
Some people have a longer soft palate or uvula. This can produce narrowing of the airway between the nasal cavity and throat, resulting in obstruction.
Health problems associated with snoring
Chronic snoring is associated with many serious health problems like obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA). OSA is characterized by interruption of breathing during sleep which lasts for more than ten seconds. More than five such episodes per night occur in these patients. There is blockage of the airway which is partial or complete. As a result of this, the person wakes up from sleep frequently. Due to repeated disturbance in sleep, deep sleep is not attained and these patients wake up tired. It adversely affects performance at work and the quality of life. Scientific studies have shown that OSA is associated with hypertension, ischemic heart disease, diabetes mellitus, and stroke.
Obesity and snoring
Snoring is commonly found in obese people. Obesity is a major risk factor for OSA. The increased fat deposition around the neck and pharynx leads to narrowing of the airway.
Clinical assessment
Fiberoptic endoscopy of the upper airway which includes the nasal cavity and nasopharynx is essential for the assessment of these patients. This examination is performed in awake and asleep patients. The examination is done in multiple positions to see changes in the airway which may occur during various positions during sleep. The aim is to identify the level of obstruction like nasal, at the level of the soft palate, or in the pharynx.
Sleep video-endoscopy is another very useful technique as it records videos of movements of the airway during sleep. This technique has greater potential for identifying the site of obstruction because it more closely reflects airway changes during sleep. It is also useful for directing surgical intervention.
Preventive step
Snoring may just be a sound produced during sleep or a feature of an underlying disorder. If it affects your life or the life of people around you, it calls for a medical consult. There are many serious health risks associated with snoring and correction of these can surely improve the quality of life.